… oder der neue Mining Goldrausch mit Crypto – Währungen.
Bitcoin Mining hat sich in den letzten Jahren deutlich verändert. Zuerst experimentiert man mit seiner eigenen CPU, dann nutzte man seine Grafikkarte und zum Schluss begann der Krieg der ASIC Miner. ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit).
Wer mit dem ASICs Mining Geld macht, entschied sich weitgehend anhand der Stromkosten und wer neue effiziente Modelle herstellen konnte. Daher verwundert es nicht, dass nur noch dort wo der Strom billig war, mehr und mehr Miner sich konzentrierten. Die klugen Miner gehen auch noch dahin wo das Klima kälter ist, um die kosten für die Klimatisierung gering zu halten.
Die Preisbewegungen und der Boom der Cryptos in der ersten Jahreshälft 2017 hat die Karten für einen begrenzten Zeitraum neu gemischt. Auf einmal konnte man wieder mit seinem Gaming PC profitabel Minen. Der Ethereum Algorithmus Ethash läuft aktuell am besten auf einer Spielegrafikkarte, die Gewinne reichten aus um auch in Länder mit hohen Stromkosten die laufenden Kosten zu kompensieren.
Der Mining Markt kam in Bewegung, immer mehr private Miner bauten sich Mining Rigs, auf youtube gibt’s eine menge Filme dazu mit sehr spannenden Konstruktionen und die Motherboard und Grafikkarten Hersteller produzieren Gaming Hardware die nur noch für das Minen ausgerichtet ist.
Am besten lässt sich der Minig-Boom am Verlauf der produzierten Hashrate im Ethereum Netz über die Zeit, oder dem Aktienverlauf von Nvidia ablesen.
https://etherscan.io/chart/hashrate
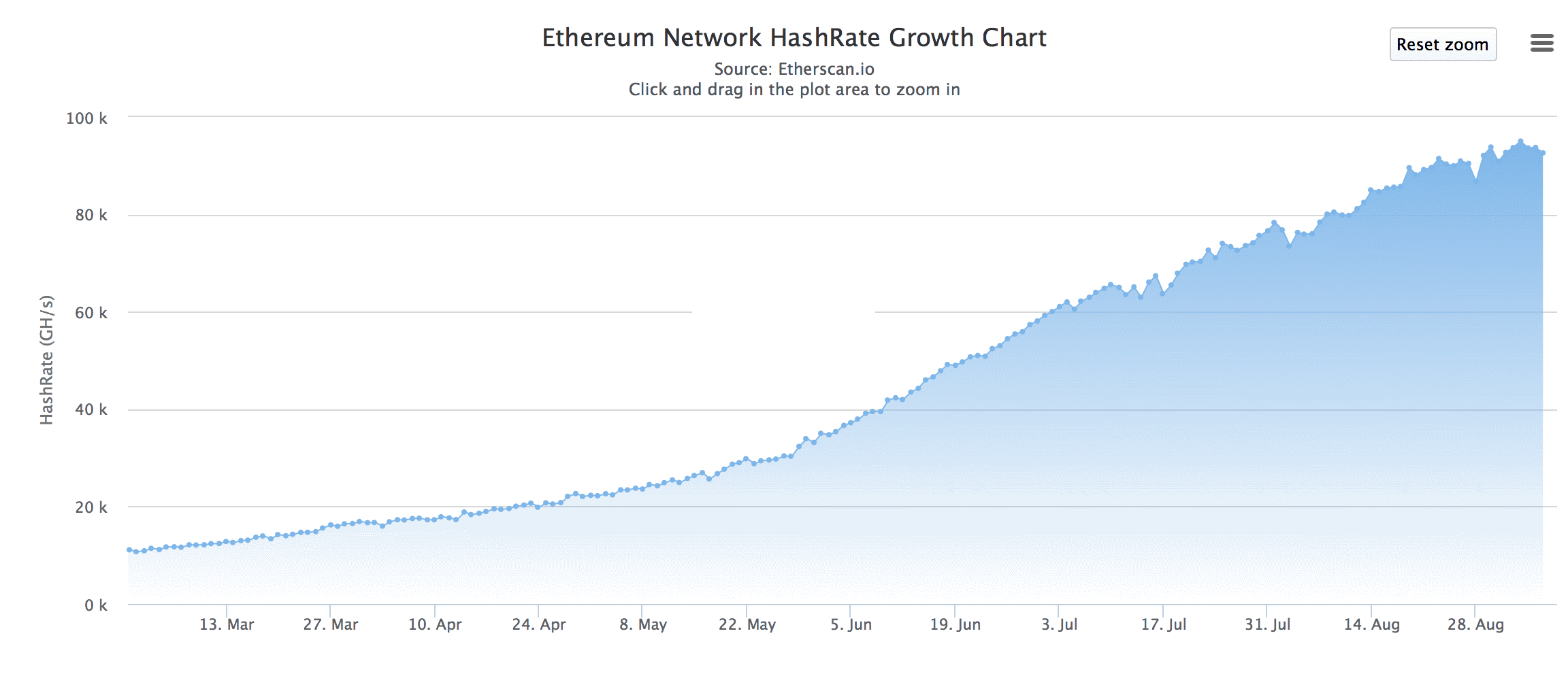
Stand 7.9.2017 werden ca. 90 tera Hashes im Ethereum Netzwerk fürs Mining erzeugt. Eine Nvidia Geforce 1070 generiert ca. 30 Mega Hashes, d.h. alleine für Ethereum würden aktuell alleine 3 Mio. Grafikkarten verwendet. Die Karte benötigt ca. 100 Watt wenn sie richtig eingestellt ist, also werden mindestens 300 Megawatt für das Ethereum Netzwerk verbraucht. Eine durchschnittliche Windkraftanlage erzeugt 3 MW, d.h. min. 100 Windräder laufen nur für Ethereum.
Die meisten verwendeten Karten erzeugen weniger Hashes und verbrauchen mehr Strom.
Die verwendeten Algorithmen unterscheiden sich stark im Stromverbrauch, So benötigt das Minen der Währung Monero weniger Leistung, Ethereum liegt im Mittelfeld, wohingegen Zcash 10..20 % mehr Energie aufnimmt. Jede Währung hat eine eigne optimale Configuration von Leistung, Speicher- und GPU Taktrate.
Das Minen von Ethereum hat einen weiteren Pferdefuß. Nicht nur die stark wachsende Anzahl der Mining-Grafikkarten reduzieren die Erträge, auch die „difficulty bomb“ im Code sorgt für fallende Erträge. Sie macht das Mining schrittweise unattraktiver bis zum nächsten Release, in dem der Konsen-Algorithmus auf Proof-of-Stake umgestellt wird.
Auf der folgenden Website wird der Effekt deutlich:
http://www.mycryptobuddy.com/EthereumMiningCalculator
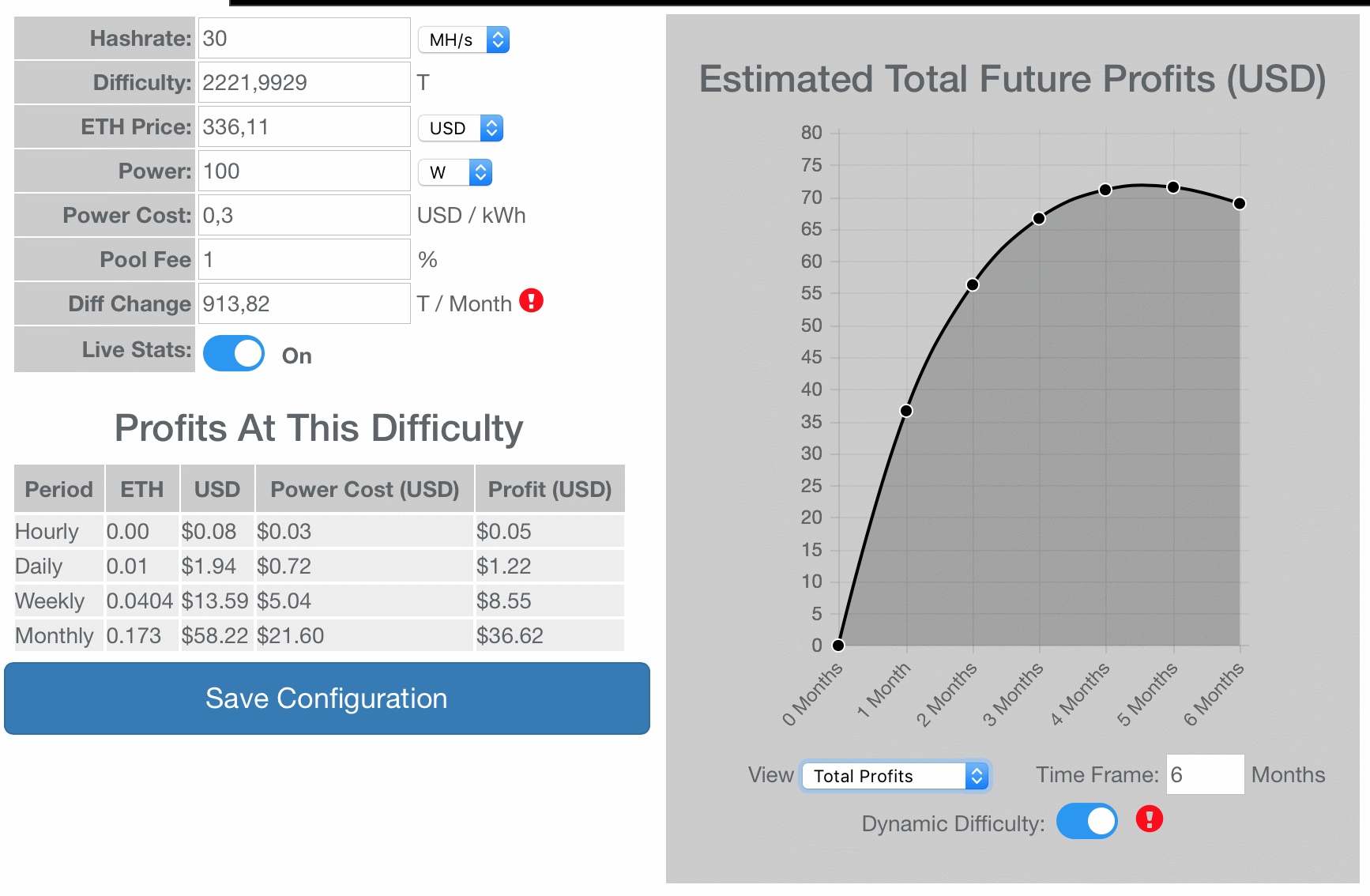
Andere Cryptos haben zwar keine „difficulty bomb“ und bleiben beim Proof-of-Work, es ist jedoch zu beobachten, dass der Hashrate Markt sehr effizient ist, Ethereum Miner wechseln zu Zcash, Monero etc. so dass die Mining-Erträge dort analog sinken und sich dem Strompreis nähern.
Welcher Coin welchen Algorthmus verwendet findet man unter anderen auf whattomine.com oder bei der Börse cryptopia.co.nz.
Die Preise für Mining geeignet Grafikkarten ist ebenfalls im Sommer schnell angestiegen um bis zu 50 %, sinkt jetzt jedoch schon wieder, hat aber noch nicht das Mai Niveau erreicht. Glaskungeln gehen davon aus, dass sie Anfang 2018 wieder auf dem Level von vor dem Boom sind.
Wie bei jedem Goldrausch verdienen auch bei diesem die Verkäufer von Schaufeln am meisten Geld. Neben Nvidia und AMD scheinen auch die Entwickler von Miningsoftware das große Geld zu machen. Der weitverbreitete Claymore Mining-Software nutzt 1% der Mining-Zeit für den Entwickler. Das könnte bedeuten, wenn 10% der Miner die Software von Claymore verwenden, jede Grafikkarte 40 $ in Cryptos pro Monat schürft, dann würde der Entwickler 0,40$ pro Grafikkarte und Monat verdienen. Das wären bei 3 Mio. Karten einnahmen von 120.000 $ im Monat. Vermutlich verwenden jedoch mehr Grafikkarten den Claymore Miner.
Ob es sich lohnt einen Rechner fürs Minen zu bauen, muss jeder für sich entscheiden. Einen positiven Business Case auf lange Sicht zu rechnen ist schwierig, in der ersten Hälfte des Jahres 2017 hätte man mehr Geld verdient, wenn man das Kapital für einen Rechner direkt in Ether investiert hätte, jedoch ist der Spaß einen eignen Rechner zusammen zu bauen unbezahlbar.