During the last months we have seen a lot of press releases about blockchain projects everywhere, but only few of them are more then just experiments. We also saw many notes about private blockchains as a solution for enterprises. Private blockchains are a good story for consultant companies and their skin deep powerpoint writers with expensive cufflinks. However, we haven’t seen good use cases yet in all these power point slides, just repeating arguments and sales stories. So where is the real private blockchain killer application? More or less every problem addressed by private blockchains can be solved with already existing technologies and software architecture patterns.
Most IT system in enterprises follow the centralized architecture paradigm, e.g.:
a) MDM (Master Data Management), data from different sources will be collected and consolidated in central databases, then the data will be processed, checked etc. with some algorithms or human interactions and at the end the data will be distributed to different target business applications.
b) Central BPM (Business Process Management) systems will be triggered by an event, it pulls some data from other sources, process them, generate reports, trigger new events etc.
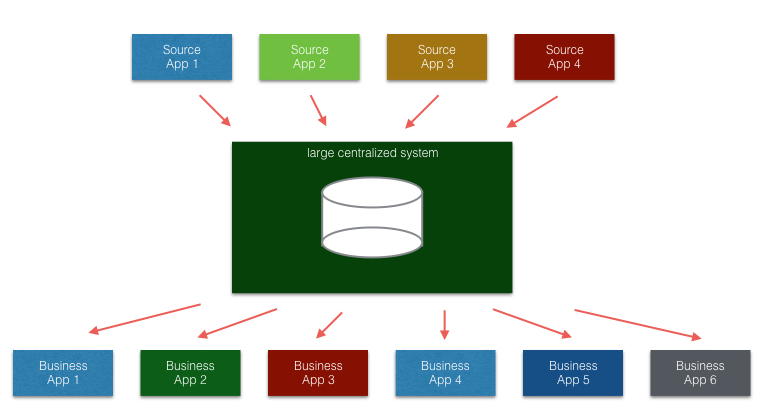
We can continue and continue to all the different other centralized systems and architecture pattern. We build centralized solutions, because we learned centralized architectures are good, however, in decentralized or silo organizations it is difficult to establish such structures. In this kind of organizational structure, we find very often poorly organized data exchanged via Excel and emails. BPM solutions perform poorly too due to the fact that it is difficult to establish and enforce exactly specified business processes.
Central systems also ignore circumstances of local data aspects, not all data has the same importance for all business applications, very often you need individual data and data rules for single data consuming business app.
How DLT (distributed ledger technologies) and smart contracts instead could help to integrate applications in a decentralized/silo organization where centralized architectures break on the organizational structure?
In a DLT-based solution there is no central system. Every business application is equal and can participate in the P2P network by contributing or consuming data from the distributed ledger. How an application contributes or how it consumes data is a local decision of the application itself. For instance, if it needs a specific frontend, it can be implemented in the context of the specific application in need of it.
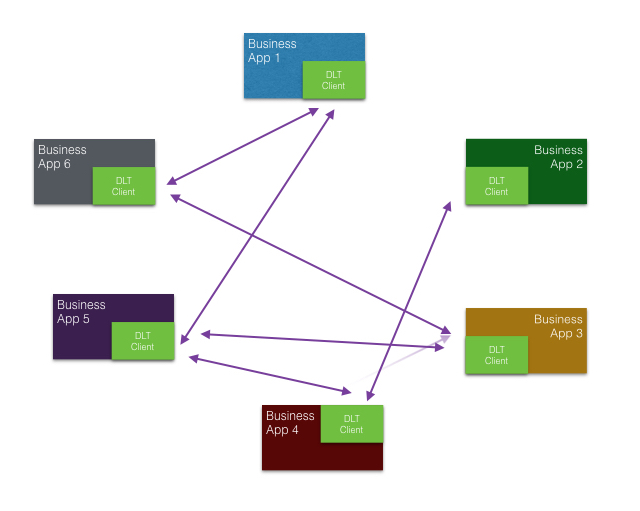
This is a new software architecture paradigm which could lead to better scalability, less redundancies and lightweight integration of applications in technologically and organizationally decentralized environments.
Relevant Articles: